25/08/2023
Language Bridges: A Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT vs. Google Bard AI in Translation

Effective communication across languages has become necessary in our interconnected world, where borders are transcended by technology. Machine translation, a branch of artificial intelligence, has taken center stage in breaking down linguistic barriers.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Translation have significantly advanced over the years. It has led to the development of generative AI, such as ChatGPT and Google Bard. But between Bard vs. Chatgpt, which is the better option?
Today, we will compare Chatgpt vs. Bard, such as technical aspects, translation accuracy, user experience, cost-effectiveness, and ethical implications. By analyzing these factors, we intend to guide users in making informed decisions when selecting it for translation purposes.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Technical Specifications
When delving into the realm of machine translation, understanding the technical underpinnings of the tools is paramount. This section provides an in-depth exploration of the technical specifications that drive the language capabilities of both Google Bard AI and ChatGPT.
The Architecture of ChatGPT Systems
At the heart of ChatGPT's language prowess lies the transformative power of the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture. Developed by OpenAI, GPT architecture leverages the potency of transformer models, which have revolutionized natural language processing tasks.
These models consist of layers of attention mechanisms, allowing them to grasp the relationships between different words within a sentence. ChatGPT, based on the GPT-3.5 variant, boasts a staggering number of parameters—175 billion, to be precise. This expansive parameter count contributes to its capability to comprehend context, syntax, and semantics with remarkable finesse. ChatGPT can seamlessly transition from English prose to French poetry by training on diverse datasets, capturing the nuances of each language's structure and expression.
The Architecture of Google Bard AI Systems
Google Bard AI, Google's contribution to the field of machine translation, also harnesses the prowess of transformer-based architectures. These systems excel in parallel processing, enabling efficient training on vast datasets.
Google Bard AI gains an understanding of syntactic and grammatical intricacies, ensuring its translations align closely with human comprehension. While the exact architecture details might not be publicly disclosed, Google's longstanding involvement in natural language processing research has likely influenced Bard AI's architecture to emphasize efficiency and accuracy.
Supported Languages
The language landscape is diverse and complex, requiring translation tools to cater to many tongues. ChatGPT and Google Bard AI rise to the challenge by offering support for many languages. These languages span continents and cultures, encompassing everything from major international languages to regional dialects.
These tools empower users to break down barriers and connect with a global audience by supporting a broad linguistic spectrum. While the exact number of supported languages may vary between the two, the commitment to linguistic inclusivity is a shared goal.
However, ChatGPT supports more language compared to Bard. If you make a request with ChatGPT it tries to provide the language you request even if it doesn't have a lot of data on the language.
ChatGPT vs. Bard: Translation Accuracy
One of the most critical aspects is the accuracy with which a system can transform text from one language to another while preserving its intended meaning. The ability of translation models to produce coherent and contextually relevant translations can significantly impact their usability and effectiveness. In this section, we will delve into the intricate landscape of translation accuracy, comparing the performances of ChatGPT and Bard, shedding light on their assessment methods, strengths across different language pairs, and their handling of complex contextual and cultural nuances.
Methods and Metrics for Testing Accuracy
Evaluating the translation accuracy of machine translation systems requires the application of rigorous methods and metrics. Two commonly employed approaches are automated metrics and human evaluations. Automated metrics, such as BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) and METEOR (Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit ORdering), provide quantitative measures by comparing machine-generated translations with reference translations.
However, these metrics might need to fully capture the nuances of human language, leading to potential discrepancies in perceived quality. Human evaluations involve human judges ranking translations based on their fluency, adequacy, and overall quality, offering a more holistic assessment of translation performance.


Comparison of Performance in Different Language Pairs
Languages exhibit various intricacies, including diverse syntactical structures, idiomatic expressions, and linguistic nuances. Therefore, the translation accuracy of machine translation models can vary significantly across different language pairs. ChatGPT and Bard have been trained on vast multilingual datasets, enabling them to tackle a multitude of languages.
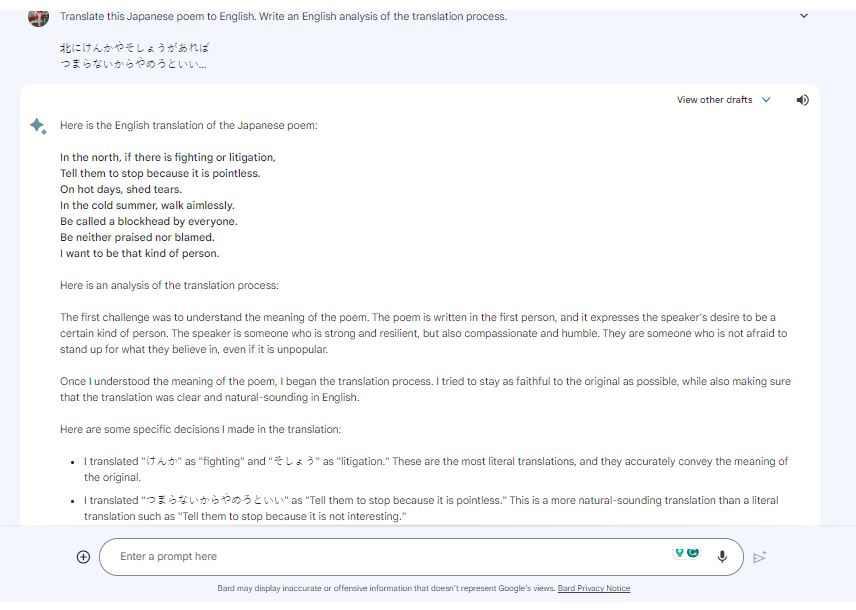

However, the effectiveness of their translation can depend on factors such as the amount of available training data for a specific language pair, linguistic similarity, and the prevalence of rare or complex linguistic patterns.


Handling of Contextual and Cultural Nuances
The accurate translation goes beyond mere word substitution; it requires understanding the context in which the text is situated. Contextual nuances, such as pronoun references, word order, and tense, can significantly affect the intended meaning of a sentence.
Moreover, cultural nuances, including idiomatic expressions and socio-cultural relations, pose additional challenges in translation. ChatGPT and Bard aim to address these complexities by leveraging their neural architectures designed to capture broader contextual information. However, the extent to which they can accurately reproduce context and cultural sensitivity influences the fidelity of their translations.
The Differences Between Bard and ChatGPT in User Experience and Interface
A pivotal factor that can significantly influence the adoption and effectiveness of a system is the user experience (UX) it offers and the interface through which users interact with it. So, we will delve into the nuances of user experience and compare the distinctive qualities of Google Bard AI and ChatGPT regarding their ease of use, integration capabilities with external tools and platforms, and the level of community engagement and support they provide.
Ease of Use
ChatGPT and Google Bard AI offer user-friendly interfaces, simplifying the translation process for users with varying degrees of technical expertise. User experience hinges on the simplicity and intuitiveness of a system's interface.
Google Bard AI is known for its streamlined interface that allows users to input text and receive translations with minimal effort. Its intuitive design caters to novice users and those well-versed in machine translation. The process of submitting text and receiving translations is smooth, enabling users to obtain accurate results swiftly.
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, offers a conversational interface that might feel more interactive. While it excels in various natural language processing tasks, its conversational nature might require users to adapt to its style. The back-and-forth interaction might be engaging for some users, but it could also involve a learning curve, especially for those accustomed to traditional translation interfaces.
Both Bard and ChatGPT can support file import. However, Bard is limited as it can only read images and webP. ChatGPT, through its code interpreter feature, can also read pdf, csv, txt, md, html, doc, images, etc., making it broader compared to Bard.
Integration with Other Tools and Platforms
Integrating these models with other tools and platforms streamlines translation workflows, enabling users to incorporate translation capabilities into their existing systems. The versatility of machine translation systems can be enhanced through seamless integration with other tools and platforms.
Both Google Bard AI and ChatGPT acknowledge the importance of integration.
Google Bard AI, being a product of Google, seamlessly integrates with the broader suite of Google Workspace tools. This integration allows users to conveniently translate documents, emails, and other content directly within the tools they already use for their work or communication. This cohesiveness simplifies the translation workflow and enhances productivity.
ChatGPT's conversational approach might require custom integration to work optimally with other tools and platforms. While OpenAI provides APIs for developers to build integrations, it might require additional effort to tailor ChatGPT's conversational capabilities to specific contexts.
Community and Support
Google Bard AI benefits from the robust Google ecosystem, which includes extensive documentation, tutorials, and user forums. Google's broad user base also facilitates community-driven support, where users can share tips, troubleshoot issues, and learn from one another's experiences.
ChatGPT, similarly, has a growing community of developers, researchers, and enthusiasts who actively engage in discussions, share insights, and provide guidance. OpenAI's communication channels and resources ensure that users have access to the information they need to utilize ChatGPT for translation and other tasks effectively.
The user experience and interface differences between Google Bard AI and ChatGPT stem from their design philosophies and intended use cases. The streamlined interface of Google Bard AI and the conversational nature of ChatGPT cater to diverse preferences and requirements.
H2: Bard vs. ChatGPT: The Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
Cost-effectiveness and accessibility are crucial considerations for individuals and businesses. Below are some concerns about the accessibility and cost-effectiveness of Bard vs. ChatGPT.
Pricing Models
The financial dimension of adopting machine translation solutions is a pivotal consideration for businesses and individuals alike. Google Bard AI and ChatGPT adopt distinct pricing models to cater to diverse user needs.
Google Bard AI is currently free. It often aligns its pricing with existing Google Workspace plans, offering users translation capabilities within the framework of their current subscriptions. This integrated approach streamlines costs for those who already rely on Google's suite of tools.
In contrast, ChatGPT offers a range of pricing tiers, including a free plan with limited usage and subscription-based models that unlock additional features and usage capacities. At $20 per month for the premium subscription, users can generate and translate more content than its free version.
Free vs. Paid Features
The differentiation between free and paid features plays a pivotal role in determining the overall value proposition of machine translation systems.
Google Bard AI's free tier often includes fundamental translation functionalities, making it a viable choice for sporadic translation needs. Its paid tiers might encompass advanced features such as enhanced accuracy, integrations, and support.
Similarly, ChatGPT offers free access to its capabilities, although with certain usage limitations. The subscription-based plans, such as ChatGPT Plus, offer benefits like faster response times, priority feature access, and higher usage thresholds. Users can thus gauge their translation requirements and decide between free offerings and premium plans that align with their specific demands.
Accessibility for Small Businesses and Individuals
The accessibility of machine translation systems to small businesses and individuals is significant.
With its integration into the Google Workspace suite, Google Bard AI provides an accessible solution for entities already immersed in Google's ecosystem. This integration enables users to seamlessly incorporate translation into their existing workflows, enhancing efficiency and reducing barriers to adoption.
ChatGPT, with its diverse pricing tiers, ensures accessibility for a broad range of users. The availability of a free plan is particularly appealing to small businesses and individuals seeking an entry point into machine translation without upfront costs. As their translation needs evolve, they can opt for subscription plans that offer expanded features and capabilities.
The Ethical Considerations for Using ChatGPT and Bard in Your Translation Process
Integrating machine translation systems like ChatGPT and Google Bard AI into the translation process introduces a spectrum of ethical considerations that extend beyond technical functionality. Below, we will explore the moral landscape surrounding the use of these systems, highlighting the critical aspects of data privacy, potential bias in translation outcomes, and the environmental impact associated with their utilization.
Data Privacy
Both ChatGPT and Google Bard AI handle sensitive user data, warranting transparent data privacy practices to ensure user trust. However, concerns regarding data privacy emerge when sensitive or confidential information is subjected to machine translation. Users must be vigilant about these systems' security measures to safeguard the data they process.
Bias in Translation
Mitigating biases in translation is a shared challenge for these models, requiring continuous efforts to eliminate stereotypes and inaccuracies. However, the training data carries inherent biases. These biases can be perpetuated in translated content, amplifying stereotypes and perpetuating discriminatory language.
Environmental Impact
The energy consumption of AI models has raised concerns. As users, understanding and minimizing the environmental impact of these tools is essential. Machine translation models like ChatGPT and Google Bard AI are resource-intensive, requiring significant computational power to function effectively. The ethical concern here revolves around the carbon footprint associated with their operations, which users should consider when using.
Final Thoughts
This Google Bard vs. Chatgpt comparative analysis has highlighted their technical architectures, translation accuracy, user experience, cost-effectiveness, and ethical considerations. As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, both models are likely to undergo enhancements and improvements. Ultimately, the choice between ChatGPT vs. Google Bard AI depends on individual needs, preferences, and the context of translation requirements. By carefully weighing the factors outlined in this study, users can confidently select the language bridge that best aligns with their goals.